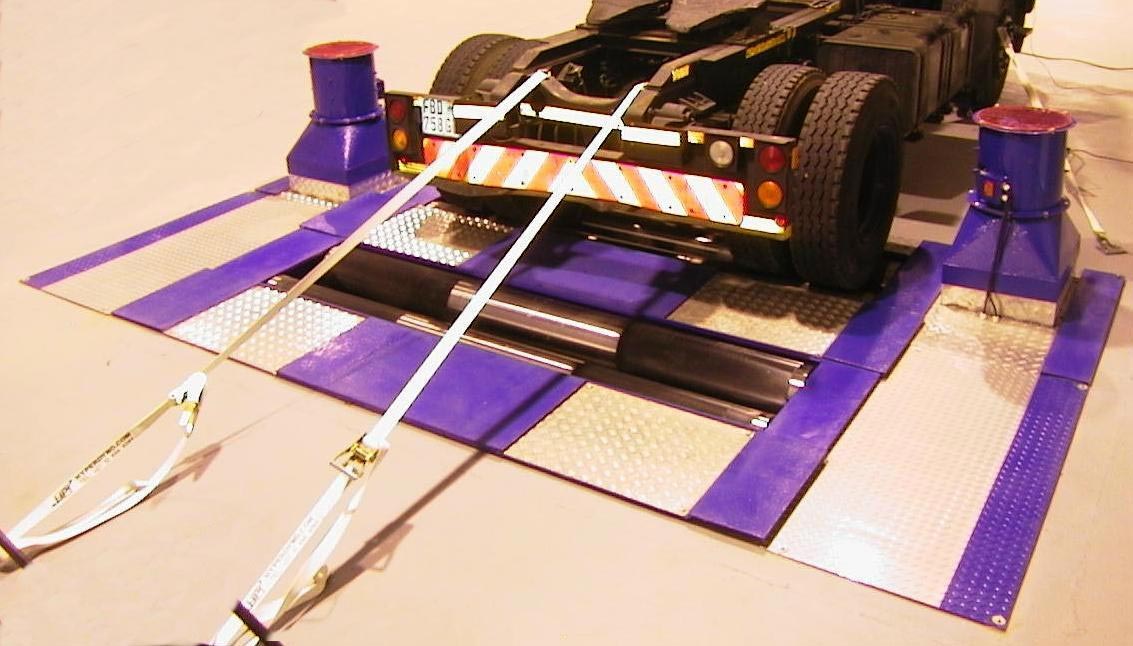
Fleet Fuel Efficiency: Optimising Trucks With Dynos
Fleet operators are throwing money away. Dynos reveal what road tests miss—and how much you’re losing.
Most operators believe routine maintenance prevents engine failure. They’re only half right. Overlooked testing protocols don’t just cause premature breakdowns—they trigger emissions violations that invite regulatory fines and damage your reputation. The difference between engines running flawlessly for years and those failing catastrophically often comes down to one overlooked practice. Discover which testing standards separate industry leaders from those constantly battling downtime and compliance issues.
Engine testing compliance exists not as bureaucratic obstruction, but as the foundation upon which safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible diesel operations rest.
Stationary engines exceeding 500 horsepower require performance testing every 8,760 hours or three years, ensuring engine performance remains within regulatory parameters. Our state-of-the-art testing facilities enable precise measurement of these critical performance benchmarks.
Skipping mandated testing creates cascading consequences. Failing emissions tests triggers fines, registration denial, and costly repair mandates. Non-compliance prevents vehicle registration renewal and raises regulatory implications for entire engine families. Engines constructed after 11 July 2005 fall under NSPS requirements and must maintain certified status to avoid enforcement actions.
Poor testing practices allow excess nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter to accumulate, compromising air quality standards and contributing to Clean Air Programme failures.
Professional operators realise that compliance protects both their operations and their communities. Regular testing maintains engine performance standards while demonstrating environmental stewardship.
Most diesel testing facilities operate with specialised cells, each configured for a narrow range of engine sizes and types, creating inefficiency and limiting operational flexibility.
Identical cell design eliminates this fragmentation. A single, universally configured test cell handles engines from modest outputs to 1,200 HP, removing the need for multiple dedicated spaces. This standardisation simplifies facility planning and reduces construction costs.
Standardised cell design consolidates engine testing across all power ranges, eliminating facility fragmentation and reducing construction costs.
Engine capacity flexibility becomes a competitive advantage. Facilities can accept diverse client projects without routing work elsewhere. The same cell accommodates small diesel units, medium-duty engines, and high-performance applications through adjustable absorption systems and modular sensor configurations.
Mechanisation improves this versatility further. Fully mechanised cells require no operator presence during testing, reducing labour demands while maintaining precision across varying specifications. Identical test cell design ensures that all engines can be tested in any cell without reconfiguration, maximising operational flexibility and asset utilisation. Our cutting-edge software solutions provide real-time monitoring and data analysis across all test configurations.
TracVeyor systems optimise material handling, supporting rapid test cycles regardless of engine type or horsepower rating.
Identical test cells that accommodate engines across a wide horsepower range demand equally consistent input—fuel quality that meets strict parameters every single time.
Fuel degradation directly undermines testing accuracy and engine performance, making testing frequency essential to reliable diagnostics.
Before each run, operators should verify cetane rating, sulphur content, water and sediment levels, viscosity, and oxidative stability. ASTM D975 standards establish certification benchmarks for these critical measurements. A minimum cetane rating of 40 guarantees proper ignition quality, while ultra-low sulphur diesel at 15 ppm limits emissions and corrosion.
Viscosity between 1.9-4.1 mm²/s prevents injector wear and combustion inefficiency.
Regular fuel quality testing prevents black smoke, incomplete burning, and equipment failure. This systematic approach protects your investment and assures repeatable, scientifically valid results across all testing protocols. Establishing consistent testing schedules maintains compliance with regulatory standards and ensures engine reliability throughout extended operational periods.
Regulatory compliance in diesel engine testing requires precise measurement of three critical emissions parameters: nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and particulate matter (PM).
Chemiluminescence methods deliver accurate NOx measurement per ISO 8178-1 and EPA Method 7E standards, essential for establishing baseline compliance data.
CO₂ analysis integrates within multi-gas systems on ASM dynamometers, with mechanised air/fuel ratio calculations and dilution corrections applied throughout testing phases. Hyper Power International’s dynamometer systems provide the precision infrastructure necessary for accurate multi-gas analysis and emissions testing.
Particulate emissions evaluation employs gravimetric analysis as the certification standard, utilising full-flow dilution tunnels with weighed filters for passenger vehicles and partial-flow systems for commercial applications. Modern measurement techniques must account for the volatile fraction of diesel PM, which becomes increasingly significant in low-emission engines where semivolatile species condense onto particle surfaces during cooling and dilution stages.
EPA and CARB standards establish specific thresholds through NTE zone limits and MAW-based bins, ensuring thorough compliance testing across all operating conditions and fuel qualities.
While laboratory measurements of emissions provide critical baseline data, the true performance of large diesel engines emerges only when subjected to the transient operating patterns and variable loads they encounter in actual field applications.
Load bank testing protocols and duty cycle validation methods bridge this gap, enabling engineers to assess how engines respond to fluctuating speed changes, sudden torque demands, and sustained high-load scenarios that characterise real-world operation. Real-time data collection during these dynamic tests ensures accurate performance evaluation. In marine applications, small internal grids create particularly challenging conditions that require rapid engine response to maintain stability and reliability.
Because real-world diesel engines operate under constantly changing load conditions rather than steady-state scenarios, testing protocols must accurately simulate these fluctuating duty cycles to produce meaningful performance data.
Transient patterns demand specialised measurement approaches that differ fundamentally from steady-state testing methods.
Standard transient cycles like the FTP, WHTC, and ETC establish industry-recognised structures for evaluating engine performance across varied operating conditions.
These cycles require advanced dilution sampling techniques, including Constant Volume Sampling and full-flow dilution tunnels, to capture accurate emissions measurements during rapid load changes.
Proper test cycle arrangement, beginning with cold-start stabilisation and progressing through weighted segments, guarantees thorough performance evaluation.
Dynamometer systems must respond precisely to sudden load variations, maintaining frequency and voltage stability within established tolerances.
Tailored accessory solutions designed for specific dynamometer models enhance the system’s capability to replicate these complex transient patterns accurately.
This rigorous approach validates engine efficiency and emissions compliance under realistic automotive duty cycles.
Load bank testing represents a critical methodology for validating diesel engine performance under real-world operating conditions, moving beyond the limitations of idle-speed or light-load evaluations.
This testing protocol approach applies graduated load stages at 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% of rated capacity, with each stage maintained for 10–30 minutes while monitoring voltage, frequency, oil pressure, and exhaust temperature.
Full load operation at 100% rated load must be sustained for 60 minutes minimum to confirm steady-state performance.
Diesel systems require at least 2 hours of annual load bank testing to burn off soot and moisture effectively.
These protocols reveal cooling, fuel delivery, and alternator issues invisible during idle operation, ensuring thorough engine validation and preventing wet stacking in exhaust systems. Partnering with experienced dynamometer service providers ensures advanced diagnostic tools and customised testing solutions are applied throughout your validation process.
Static load bank testing, while essential for baseline performance assessment, cannot fully replicate the changing demands placed on diesel engines in actual field operation.
Thorough duty cycle validation techniques bridge this critical gap, ensuring engines perform reliably across real-world scenarios.
Modern validation employs both steady-state and transient operation testing, utilising type approval and real-world duty cycles to assess performance accurately.
Engineers determine regeneration frequency using in-use operating data or laboratory repetitive tests, capturing authentic operating patterns.
Direct fuel-flow measurement records speed, torque, and consumption across each duty cycle interval, providing measurable data for analysis.
Duty cycle optimisation requires evaluating service accumulation characteristics and applying sound engineering judgement based on emissions data timing.
Custom dynamometer systems with tailored software solutions enable precise simulation of these complex duty cycles, ensuring comprehensive validation across diverse testing scenarios.
This thorough approach guarantees diesel engines meet performance expectations in demanding field conditions.
Modern diesel engine testing demands precise, immediate comprehension into how an engine actually performs under operating conditions.
Real-time monitoring systems integrate seamlessly with engine control units, capturing NOx levels, exhaust gas temperature, and combustion efficiency data instantaneously. This emissions analysis capability eliminates delays in identifying engine problems, reducing operational downtime considerably.
Operators receive instant results without requiring advanced training, thanks to turnkey solutions designed for accessibility.
Visual and acoustic alarms alert technicians when values exceed preconfigured thresholds, triggering timely maintenance interventions before failures develop.
Data logging stores extensive incident records for compliance documentation and trend analysis, supporting predictive maintenance scheduling across diesel engine fleets. Regular software updates enhance system reliability and unlock new capabilities for evolving testing requirements.
Because diesel engines operate under vastly different conditions during actual use versus idle periods, regulatory bodies mandate periodic load bank testing to guarantee generators and industrial diesel systems remain reliable when demands peak.
NFPA 110 compliance verification requires full load bank testing every three years for Level 1 and Level 2 systems. During these triennial tests, operators run engines at 30% nameplate kW rating or greater for extended durations, typically four hours.
This testing frequency prevents wet stacking—the accumulation of unburned fuel in diesel engines—ensuring peak combustion efficiency.
Professional facilities executing regular testing schedules demonstrate commitment to regulatory adherence. Load bank testing burns off soot and moisture at designed operating temperatures, simulating real-world power outage conditions. Investing in professional certification for operators ensures that testing protocols are executed with mastery and accuracy, enhancing both reliability and compliance outcomes.
Facilities meeting these compliance requirements maintain federal certification and operational readiness during emergencies.
Fleet operators are throwing money away. Dynos reveal what road tests miss—and how much you’re losing.
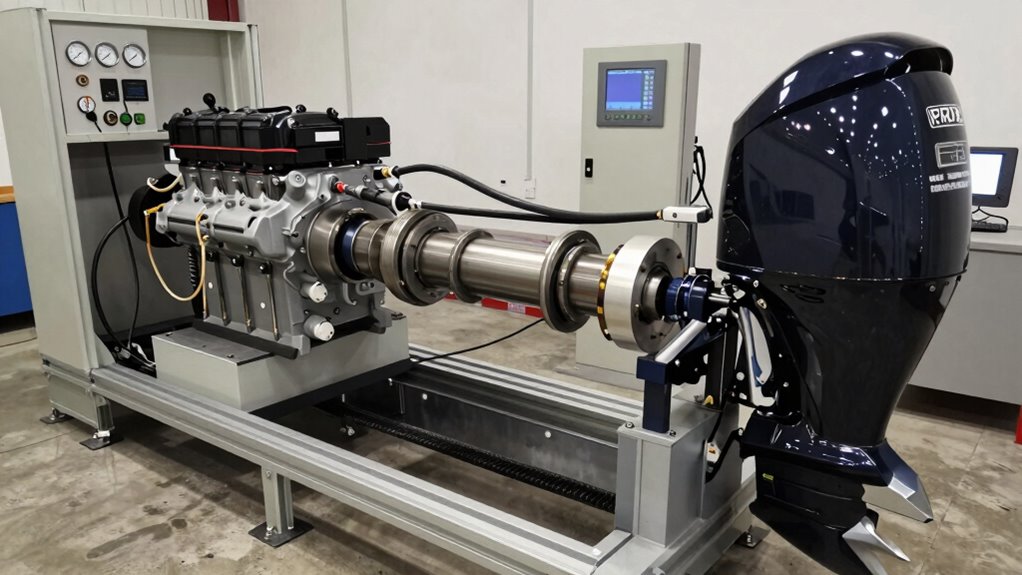

Water testing won’t reveal what dyno testing exposes. Learn why engine builders skip this step at their peril.
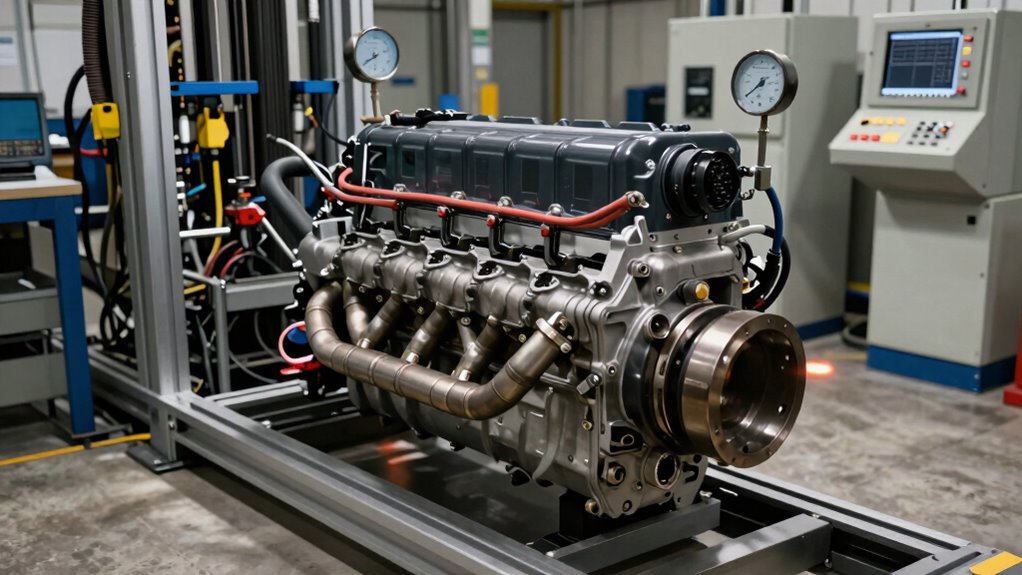

Tractor performance tests reveal what manufacturers won’t tell you. See how dynamometer data exposes hidden inefficiencies in your equipment.
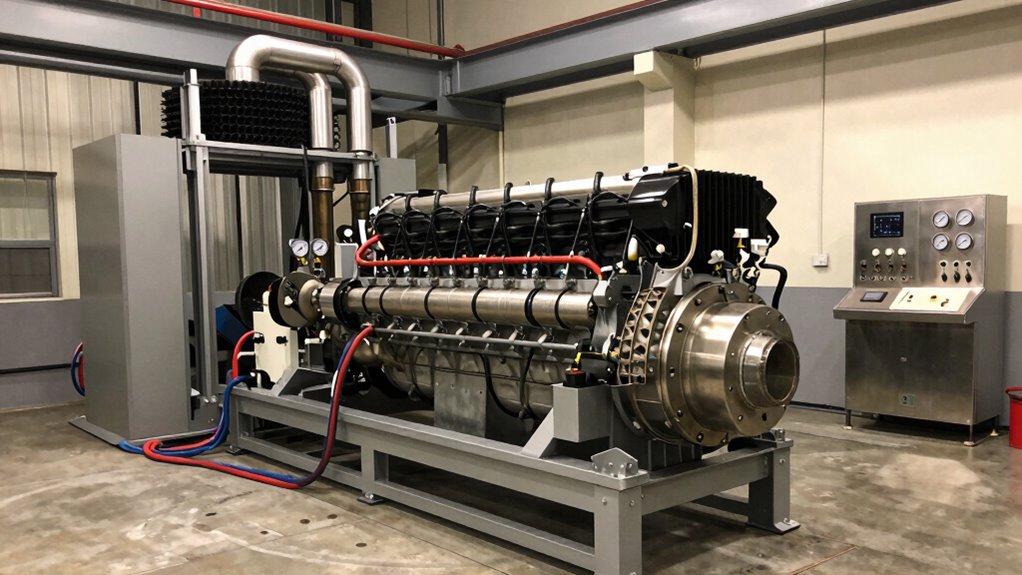

Diesel engine testing mistakes cost thousands monthly. Learn what separates thriving operations from regulatory nightmares.
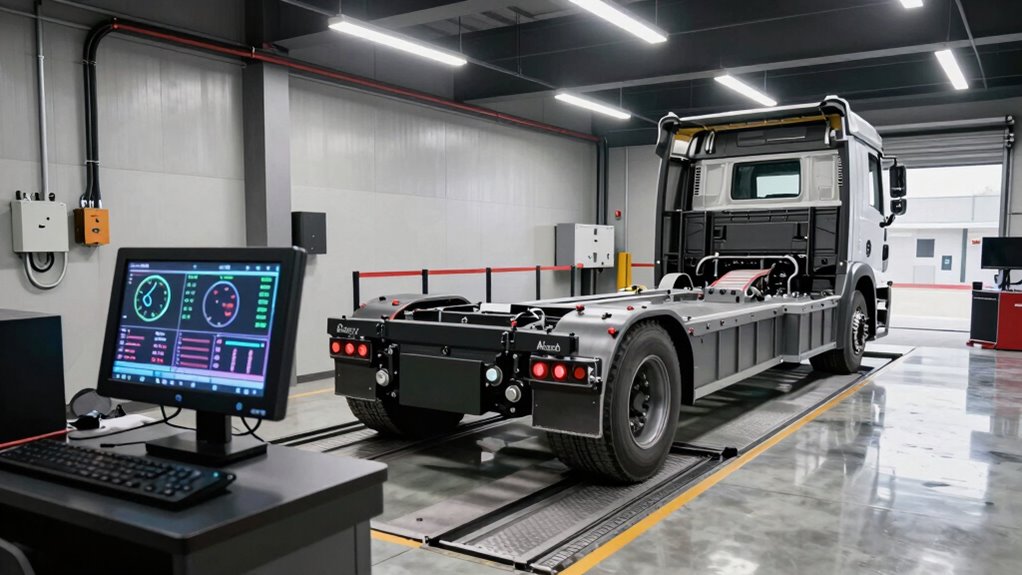

Build a diesel dyno empire while most workshops fail—here’s what separates winners from the rest.

Most dyno operators ignore this one calibration step—and it’s costing them thousands in poor data.

Force and torque aren’t opposites—they work together in ways most people misunderstand. Learn how this relationship transforms machine performance.
Your engine’s power never reaches your wheels—here’s why and what it costs you.