Dyno Cooling: Preventing Overheating in Diesel Runs
Most diesel dyno operators ignore this—and it costs them thousands in failed runs and wasted data.
Meta Description:
Your dyno testing setup could be worthless by 2026. As electric and combustion powertrains demand radically different measurement protocols and compliance structures, testing facilities face an uncomfortable truth: the one-size-fits-all approach is dead. Choose wrong now, and you’re stuck maintaining obsolete equipment while competitors race ahead with specialised systems built for tomorrow’s vehicles.
Although dynamometers have proven essential for testing internal combustion engines for decades, the fundamental shift towards electric and hybrid powertrains has exposed critical testing limitations in traditional equipment.
Standard ICE dynos lack four-quadrant capability, which regenerative braking demands during EV operation. Water brake and eddy current systems cannot deliver the precise speed and torque control that electric motors require, creating a significant gap in dynamo capabilities.
Traditional ICE dynamometers measure basic parameters like speed, torque, and temperatures without the clinical precision EVs demand. Electric motors generate significant harmonic distortion in power output that standard equipment cannot accurately measure. Comprehensive data collection across a range of conditions ensures that advanced testing methodologies can properly evaluate electric motor performance characteristics.
Electric powertrains operate bidirectionally, requiring equipment that handles motoring and loading in both directions—functionality absent in conventional setups.
Battery simulation, regenerative efficiency testing, and multi-unit communication protocols represent entirely different testing requirements, fundamentally incompatible with legacy ICE infrastructure.
The incompatibility between traditional ICE dynamometers and electric vehicle testing systems extends far beyond mechanical capability—it fundamentally shapes the protocols, measurement standards, and compliance structures that govern each testing domain.
ICE dynamometers and EV testing systems differ fundamentally in protocols, measurement standards, and compliance structures across powertrains.
ICE testing prioritises emission measurement, fuel consumption analysis, and combustion pressure monitoring through established dyno calibration standards.
EV protocols demand entirely different parameters: range testing, regenerative braking efficiency, and thermal battery performance assessment.
Testing accuracy requires specialised equipment customised to each powertrain. Our comprehensive parts and maintenance kits ensure that your testing infrastructure remains optimised for your specific application requirements.
Battery test systems evaluate charge cycles and discharge rates for EVs, while pressure sensors monitor combustion in ICE engines.
Environmental chambers simulate extreme conditions for EV components; chassis dynamometers measure ICE acceleration and efficiency.
These divergent compliance structures reflect fundamental powertrain differences.
Professionals entering either field must grasp that equipment specifications, calibration procedures, and measurement protocols remain distinct and incompatible across vehicle types. Stricter emission standards create additional compliance requirements that ICE vehicles must satisfy through enhanced testing protocols and documentation procedures.
As global emissions structures tighten and electrification accelerates, dynamometer systems face unparalleled structural demands that fundamentally reshape how manufacturers and service providers design, build, and implement testing equipment.
Regulatory impacts are driving dyno evolution across multiple fronts. WLTP and US06 compliance requires low-inertia chassis dynos with advanced roadload simulation capabilities, while BEV testing demands bi-directional power stages and battery emulators. Post-processing pipelines now deliver audit-ready datasets for regulatory compliance. The integration of climatic chambers and road simulators with dyno systems further enhances testing environments to meet stringent regulatory requirements. Hyper Power International remains at the forefront of precision dynamometer technology as these regulatory demands intensify.
Key pressures reshaping dyno design:
These design shifts guarantee testing facilities remain competitive and compliant through 2026 and beyond.
Electric vehicle dynamometers prioritise efficiency metrics—torque response, power recovery, and driving range—because EVs operate through regenerative systems and require real-time monitoring of high-voltage powertrains.
Internal combustion engine dynos, by contrast, focus on emissions compliance measurements, including NMOG + NOx outputs and carbon validation, since regulatory standards demand precise tracking of harmful pollutants during standardised test cycles. As test facilities adapt their infrastructure, high-voltage safety protocols have become essential for validating electric and hybrid vehicle performance alongside traditional emission assessments. Proactive system monitoring helps facilities maintain accuracy across both powertrain types during extended testing campaigns.
Comprehending these distinct measurement priorities reveals why modern testing facilities must utilise specialised equipment designed specifically for each powertrain technology.
While internal combustion engines have long been evaluated through emissions testing and fuel consumption metrics, electric vehicles demand an entirely different measurement structure centred on energy conversion and battery performance.
EV performance evaluation requires specialised metrics that capture motor effectiveness, energy conversion, and thermal behaviour. Torque analysis measures rotational force produced by electric motors, validating design specifications and motor performance. Power metrics quantify total output in watts or horsepower, verifying motor capabilities.
Efficiency evaluation determines the ratio of mechanical power output to electrical input, revealing how effectively motors convert energy. Temperature monitoring tracks thermal performance during operation, identifying potential overheating issues. Speed measurement records RPM values to assess how motor speed influences overall performance outcomes. These comprehensive test systems utilise regenerative operation to return excess power to AC mains, significantly reducing overall energy consumption during extended testing cycles. Certification in these specialised testing methodologies ensures that technicians can reliably execute complex EV evaluations and maintain operational mastery across diverse testing scenarios.
Community Benefits:
Internal combustion engines operate under a fundamentally different testing system than electric vehicles, one centred on measuring harmful pollutants released during combustion rather than energy conversion efficiency.
Federal Emissions Standards Structure
The EPA establishes emissions regulations requiring dynamometer testing to measure tailpipe outputs, including CO2, NOx, and particulate matter. Vehicle testing follows fixed acceleration schedules, with computerised systems calculating emissions against model year specifications.
For 1996 and newer vehicles, OBDII testing occurs annually, ensuring compliance with Clean Air Act standards.
Evolving Requirements Through 2032
New regulations phase in progressively, with tailpipe CO2 standards reaching 80 grams per mile by 2032. Multi-pollutant standards for 2027-plus light and medium-duty vehicles target significant reductions in smog, soot, and PM2.5 emissions.
Heavy-duty engines face GHG standards under 40 CFR Part 1036, making thorough emissions testing critical for manufacturers and service facilities. Comprehensive technical support ensures that testing facilities maintain calibration accuracy and performance verification throughout the compliance period.
As dynamometer testing becomes increasingly streamlined through AI-driven workflows, both EV and ICE testing protocols benefit from predictive maintenance systems that anticipate equipment failures before they interrupt testing schedules.
Real-time data analytics platforms now process sensor inputs from hundreds of test cycles simultaneously, identifying performance anomalies and environmental factors that influence repeatability and accuracy.
This integration of machine learning with traditional dyno operations reduces manual intervention, accelerates test cycles from weeks to hours, and delivers the granular perspectives needed to validate battery efficiency in EVs and emissions control in internal combustion engines with clinical precision. Strategic improvement planning integrated into these automated systems ensures that performance optimisation continues beyond initial testing, transforming raw data into customised improvement strategies that drive continuous advancement in vehicle performance across both powertrains.
The convergence of embedded vehicle telematics and artificial intelligence has fundamentally changed how modern workshops approach maintenance, enabling technicians to identify component failures before they occur rather than after they happen.
Predictive analytics now monitors 450+ real-time signals, detecting mechanical stress with unparalleled accuracy. Maintenance optimisation through machine learning forecasts specific failures—alternators, bearings, brake components—six to twelve months in advance, with over 85% accuracy.
Modern systems utilise OEM data streams, eliminating aftermarket device dependency. Engine oil pressure patterns reveal bearing wear two to four weeks early. DPF regeneration analysis prevents costly clogging failures.
Integrating expert calibration techniques during dynamometer setup ensures that predictive maintenance systems operate with maximum precision, validating the accuracy of performance data used in AI-powered diagnostics.
Key Benefits:
This integration reshapes workshops into proactive facilities, aligning technicians with industry standards.
While predictive maintenance systems identify failures before they happen, modern dynamometer testing demands a deeper layer of intelligence—one that processes vast streams of live data and extracts actionable insights at machine speed. Real-time monitoring through telemetry analysis alters how engineers evaluate vehicle performance, capturing petabytes of diagnostic data from electronic control units and sensor arrays with sub-second latency.
| Data Source | Collection Method | Processing Speed |
|---|---|---|
| ECUs & CAN Bus | Direct vehicle integration | <1 second |
| Sensor Arrays | Multi-parameter feeds | Real-time streaming |
| Environmental Variables | Integrated peripherals | Continuous analysis |
AI-driven anomaly detection identifies deviation patterns instantly, clustering root causes across development and production environments. This capability accelerates failure analysis greatly, enabling engineers to surface critical issues earlier in testing cycles and improve safety-compliance readiness considerably. Software updates ensure your dynamometer remains compatible with evolving AI-powered analytics platforms, unlocking access to cutting-edge features that enhance real-time data processing capabilities.
Because automotive powertrains continue to diversify—from traditional internal combustion engines to fully electric motors to complex hybrid systems—selecting the right dynamometer platform has become a critical decision for workshops, tuning facilities, and engineering teams.
Dyno Selection Strategies for Your Operation
EV testing demands battery cyclers, e-motor testers, and high-voltage analysers for accurate range and thermal management evaluation. ICE platforms require emission analysers and pressure sensors focused on fuel efficiency and pollutant measurement.
Hybrid systems need versatile dynamometers capable of handling regenerative braking, electric range assessment, and mode shifts.
Hyper Powers offers personalised dynamometer systems that can be customised to align with your specific testing requirements and operational goals.
Key Platform Considerations:
Your dyno platform choice directly impacts operational capability, future scalability, and competitive positioning within the advancing automotive market.
As automotive powertrains evolve across ICE, EV, and hybrid designs, dynamometer investments must modify accordingly without requiring complete equipment replacement.
Modular flexibility enables operators to reconfigure test benches for different powertrain types, accommodating battery-in-the-loop testing and high-voltage protocols alongside conventional engine assessments.
Software versatility proves equally critical. Scalable platforms compress development cycles for emissions standards while supporting multi-powertrain configurations through programmable systems and integrated digital analytics.
Cloud-enabled test management facilitates remote collaboration and data validation across distributed facilities.
These design principles guarantee that today’s dynamometer investment remains relevant tomorrow, protecting capital expenditure while enabling rapid modification to regulatory shifts and emerging technologies.
Facilities gain competitive advantage through flexible infrastructure supporting continuous innovation.

Most diesel dyno operators ignore this—and it costs them thousands in failed runs and wasted data.

Stop wasting money on road testing. One dyno investment eliminates comebacks, builds loyalty, and outpaces competitors. Here’s why your workshop needs it.
Diesel turbo lag isn’t inevitable—modern dyno diagnostics reveal the hidden culprits stealing your power. Find out what your engine is hiding.
Fleet operators are throwing money away. Dynos reveal what road tests miss—and how much you’re losing.

Water testing won’t reveal what dyno testing exposes. Learn why engine builders skip this step at their peril.
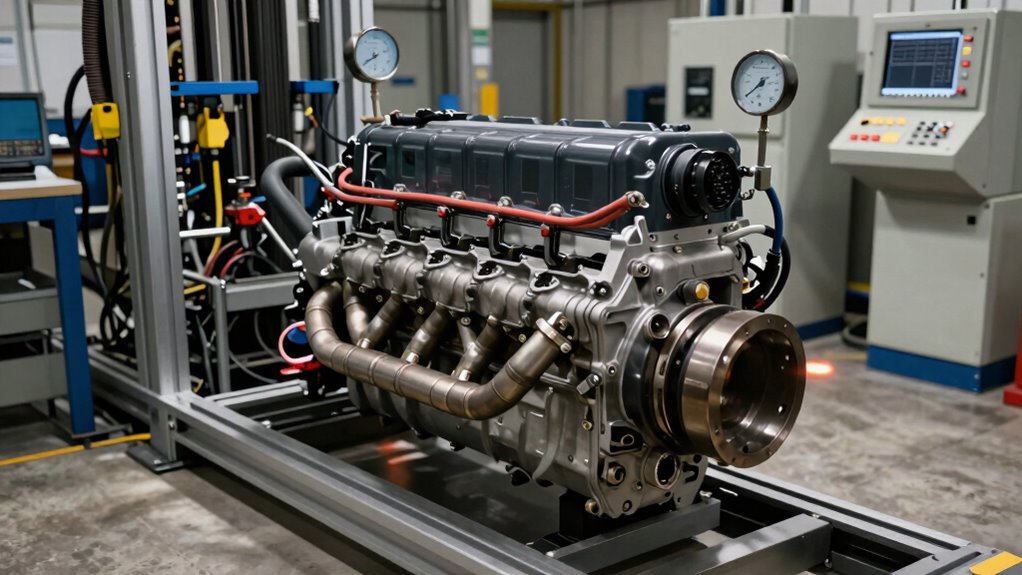

Tractor performance tests reveal what manufacturers won’t tell you. See how dynamometer data exposes hidden inefficiencies in your equipment.
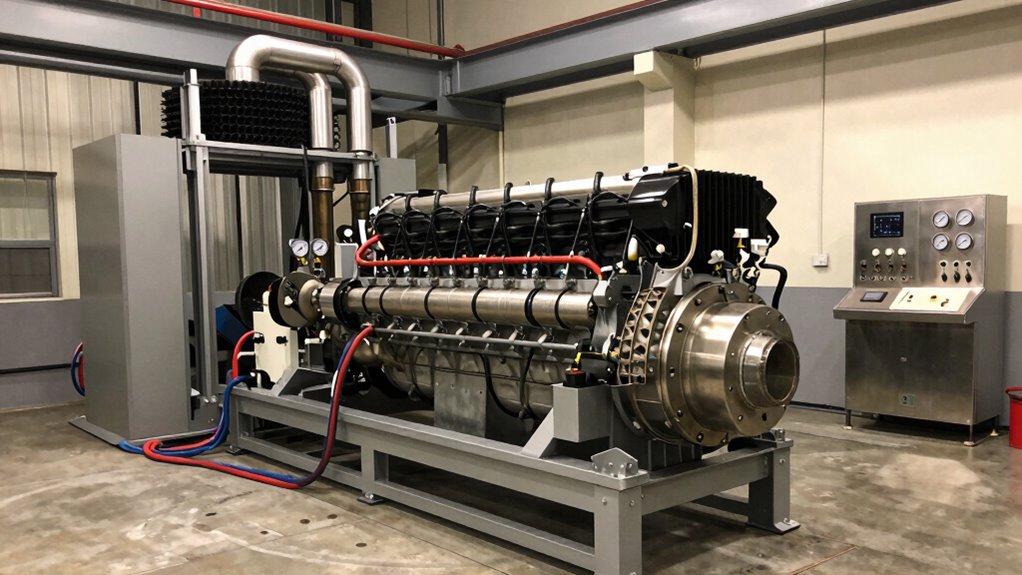

Diesel engine testing mistakes cost thousands monthly. Learn what separates thriving operations from regulatory nightmares.
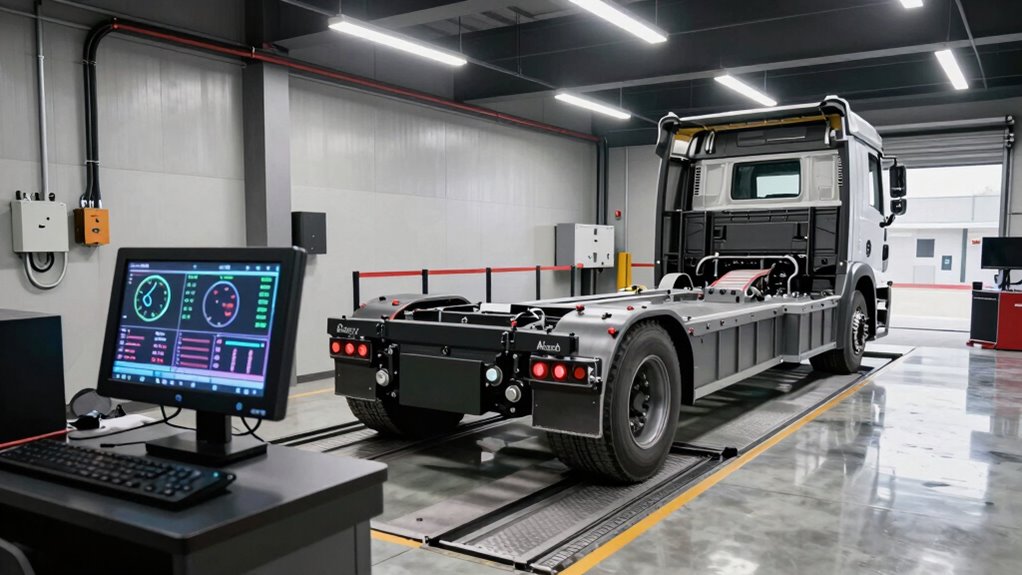

Build a diesel dyno empire while most workshops fail—here’s what separates winners from the rest.
No posts found!